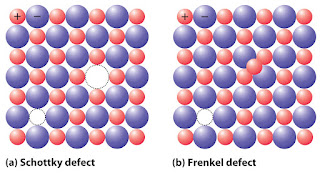
Schottky defect arise
when equal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice. It is a
common defect in ionic compounds of high coordination number* where both cations
and anions are of the same size. Due to this density of crystal decreases and
begins to conduct electricity to a smaller extent.
Examples: KBr, NaCl KCI
Frenkel
defect arises when some of the ions of the lattice occupy
interstitial sites leaving lattice vacant. This defect generally found in ionic
crystals where anion is much larger in size than the cation. Due to this
density does not change in overall composition of the crystal.
Examples:Zns, AgBr
Schottky Defect vs Frenkel Defect
Schottky Defect
1. Equal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice sites.
2. Found in highly ionic compounds with high coordination numbers and where the cations and anions are of similar size.
3. Density of the solid decreases
Frenkel Defect
1. A cation leaves the normal lattice site and occupies an interstitial site.
2. Found in ionic compounds with low coordination numbers and where the anions are much larger in size than cations.
3. Density of the solid remains the same.
* coordination number: It is defined as the number of nearest neighbours of a particle in a closed packed structure.