Phosphorylation can be defined as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to some organic compound, such as glucose and adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
Inside
the cell, the most common type of phosphorylation is the formation of ATP by
the addition of phosphate group to ADP.
There
are 3 Types of Phosphorylation occurring in a cell
Substrate
level phosphorylation
A
metabolism reaction that results in the production of ATP or GTP by the
transfer of a phosphate group from a substrate directly to ADP or
GDP.
Oxidative
phosphorylation during cellular respiration
Oxidative
phosphorylation (OXPHOS) is defined as an electron transport chain driven
phosphorylation by substrate oxidation coupled ATP synthesis through an
electrochemical transmembrane
Photo phosphorylation in Photosynthesis
The
phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP using the energy of sunlight during
photosynthesis is called photophosphorylation.
Let’s have a comparison of these 3 types.
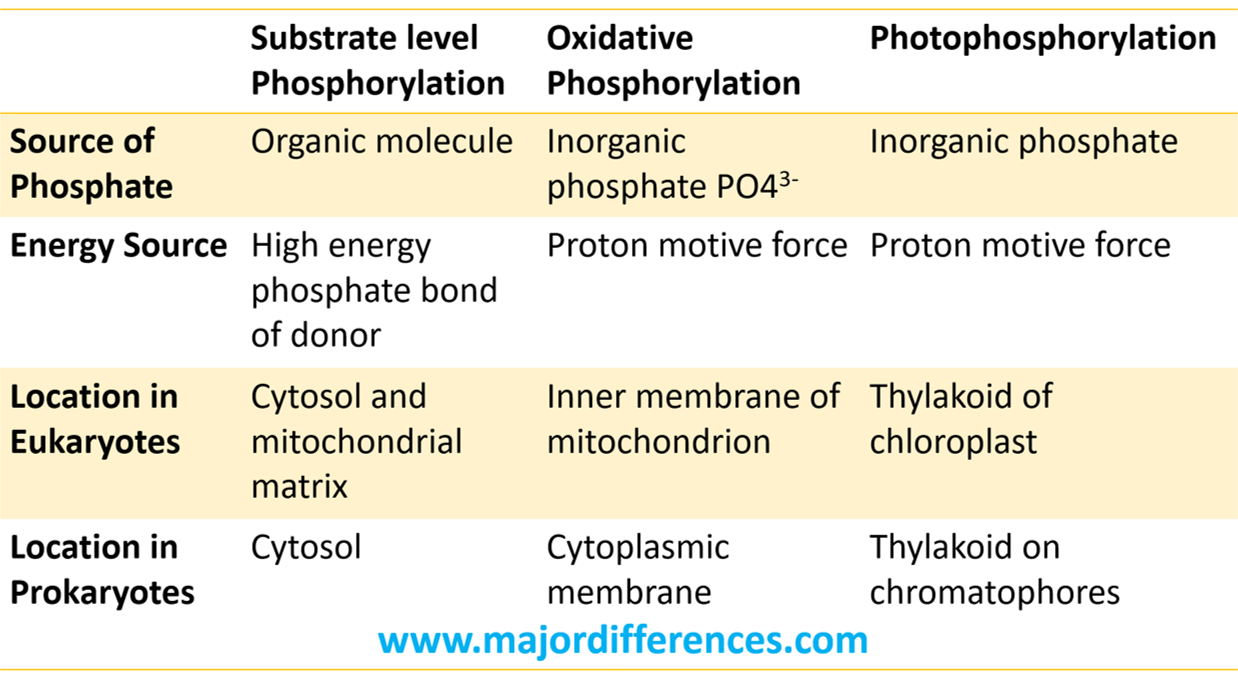
|
|
Substrate level Phosphorylation |
Oxidative Phosphorylation |
Photophosphorylation |
|
Source of Phosphate |
Organic molecule |
Inorganic phosphate PO43- |
Inorganic phosphate |
|
Energy Source |
High energy phosphate bond of donor |
Proton motive force |
Proton motive force |
|
Location in Eukaryotes |
Cytosol and mitochondrial matrix |
Inner membrane of mitochondrion |
Thylakoid of chloroplast |
|
Location in Prokaryotes |
Cytosol |
Cytoplasmic membrane |
Thylakoid on chromatophores |
|
Oxygen? |
Oxygen not |
Oxygen as terminal electron acceptor |
Oxygen evolved by photolysis of |
|
Metabolic pathway |
Common in many metabolic pathways like glycolysis, TCA cycle etc |
Cellular respiration |
Photosynthesis |
|
Pigments? |
Not involved |
Not involved |
Involved as two photosystems PSI and PSII |
Post a Comment
We Love to hear from U :) Leave us a Comment to improve this site
Thanks for Visiting.....