Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system. They are responsible for transmitting electrical signals throughout the body.
Glial cells (neuroglia) are non-neuronal cells that support neurons. They provide nutrients, remove waste products, and protect neurons from damage.
Both these cells are in brain, spinal cord and peripheral nervous system.
|
Neuron |
Neuroglia |
|
Structural and functional units of nervous
system |
non-neuronal cells that support neurons |
|
Function: Responsible for transmission of nerve impulses between
central nervous system and different parts of the body |
Support neurons by providing nutrients, positioning
the neuron, regulate their activity by controlling neurotransmitter release, removing
waste products, and protecting neurons from damage. |
|
Responsible for synaptic interactions and
electrical signaling, |
do not participate directly in synaptic interactions and
electrical signaling, |
|
Generates action potential and chemical |
No action potential and chemical synapse but has resting potential. |
|
Number: 86.1 ± 8.1 billion neurons* |
~84.6 ± 9.8 billion glial cells |
|
Neurons cannot divide once differentiated,
lack |
Glial cells can divide by mitosis even after |
|
Structure: All neurons have three different parts – dendrites, cell body, and axon. Dendrites receive messages from another Cell body has a nucleus and other organelles, maintains structure, and provide
energy and transfer signals from dendrites to axon. Axon passes the impulse to another |
They have a fibrous appearance due to thick
bundles of cytoplasmic |
|
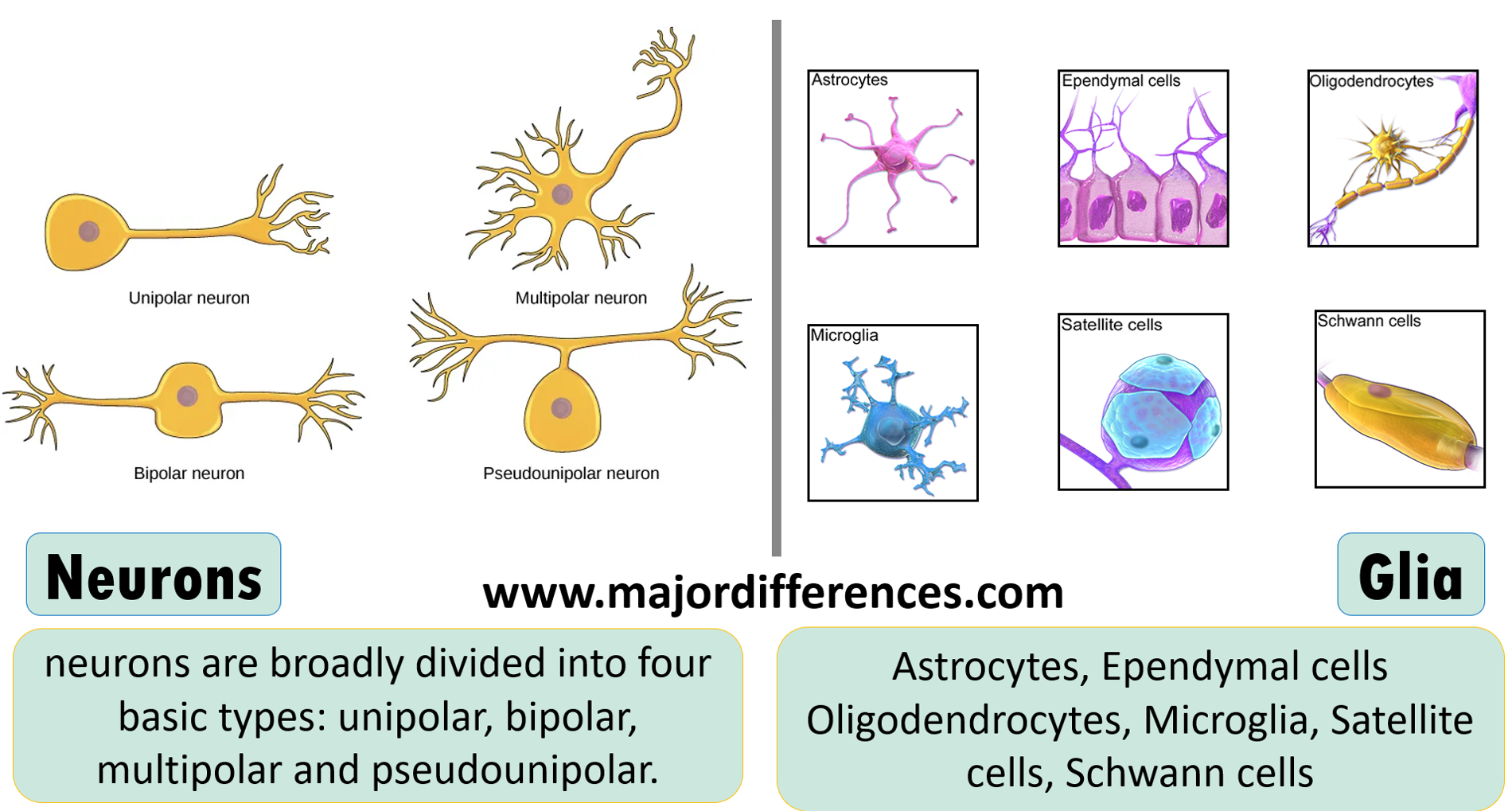
Types: Unipolar, bipolar, multipolar, and
pseudounipolar |
Astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia,
ependymal cells, and satellite cells |
Post a Comment
We Love to hear from U :) Leave us a Comment to improve this site
Thanks for Visiting.....