Difference between unipolar, bipolar and multipolar neurons
Neurons are the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system. They are responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting information throughout the body. Neurons are made up of three main parts: the cell body, the dendrites, and the axon.
Watch our video on this topic here.
- The cell body is the main part or core of the neuron. It contains nucleus and other organelles, which is the control center of the cell.
- The dendrites are the short, branching processes that receive signals from other neurons.
- The axon is the long, single process that carries signals away from the cell body.
Based on structure or number of processes, neurons are classified into
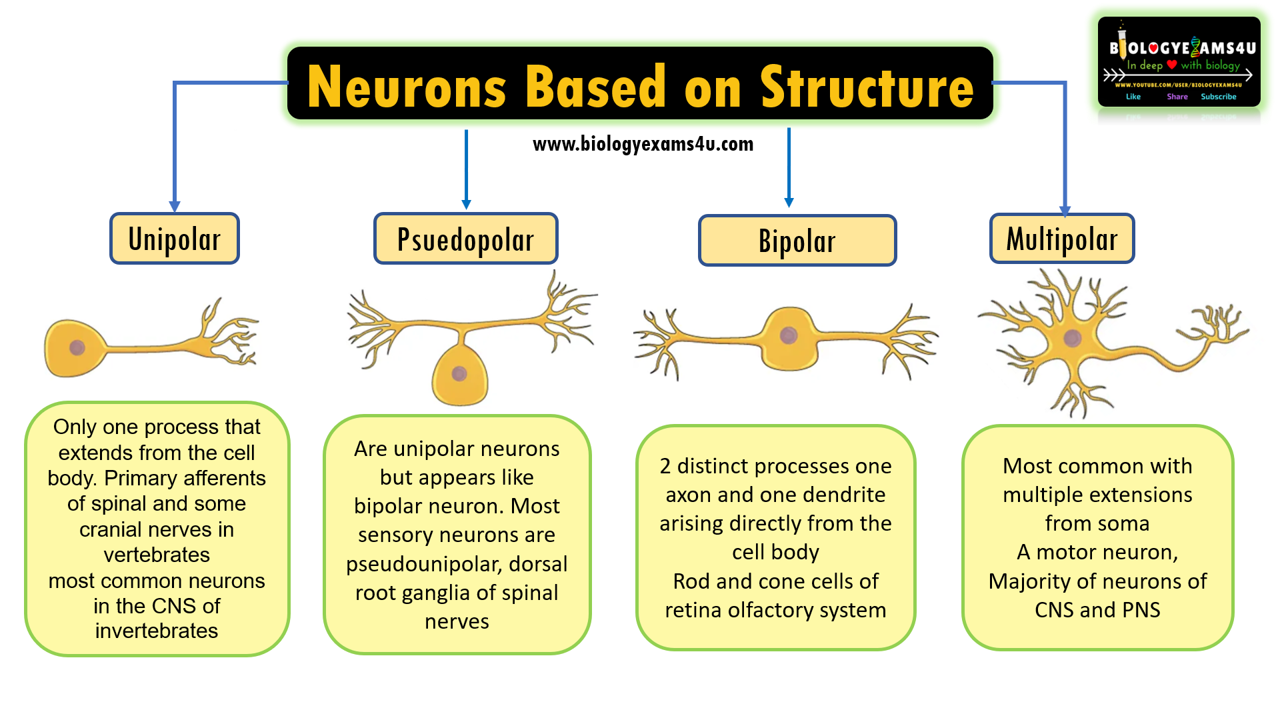
Unipolar neurons, Pseudounipolar neurons, Bipolar neurons and Multipolar neurons
In a neuron, a process is a long, thin extension of the cell body that carries signals to or from other cells (neurite). The two main types of processes in a neuron are dendrites and axons.
Unipolar neurons
- A single process or extension that extends out from the cell body, which then branches into two parts.
- The process is often an axon but branches of axons sometimes function as dendrites.
- The peripheral process is associated with sensory reception, and the central process carries the signal to the CNS.
- Unipolar neurons are found in the PNS, and they are responsible for transmitting sensory information from the skin, muscles, and other organs to the CNS.
Pseudounipolar neurons
- Are actually unipolar neurons but appears like bipolar neuron. It has a single process that extends from the soma, like a unipolar cell, but this process later branches into two distinct structures, like a bipolar cell.
- Most of which functions as axon with peripheral process functions as dendrites.
- Most sensory neurons are pseudounipolar and have an axon that branches into two extensions: one connected to dendrites that receive sensory information and another that transmits this information to the spinal cord.
- Pseudounipolar cells share characteristics with both unipolar and bipolar cells.
Bipolar neurons
- have two processes that extend out from the cell body.
- A bipolar neuron has one axon and one dendrite extending from the soma.
- Bipolar neurons are responsible for transmitting sensory information from the periphery to the CNS.
- An example of a bipolar neuron is a retinal bipolar cell, which receives signals from photoreceptor cells that are sensitive to light and transmits these signals to ganglion cells that carry the signal to the brain.
- They are found in the retina of the eye and in the olfactory system.
Multipolar neurons
- have three or more processes that extend out from the cell body.
- Each multipolar neuron contains one axon and multiple dendrites.
- They are the most common type of neuron in the human body, and they are found in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- Multipolar neurons are responsible for a wide variety of functions, including sensory perception, motor control, and learning.
- An example of a multipolar neuron is a Purkinje cell in the cerebellum, which has many branching dendrites but only one axon.
Post a Comment
We Love to hear from U :) Leave us a Comment to improve this site
Thanks for Visiting.....