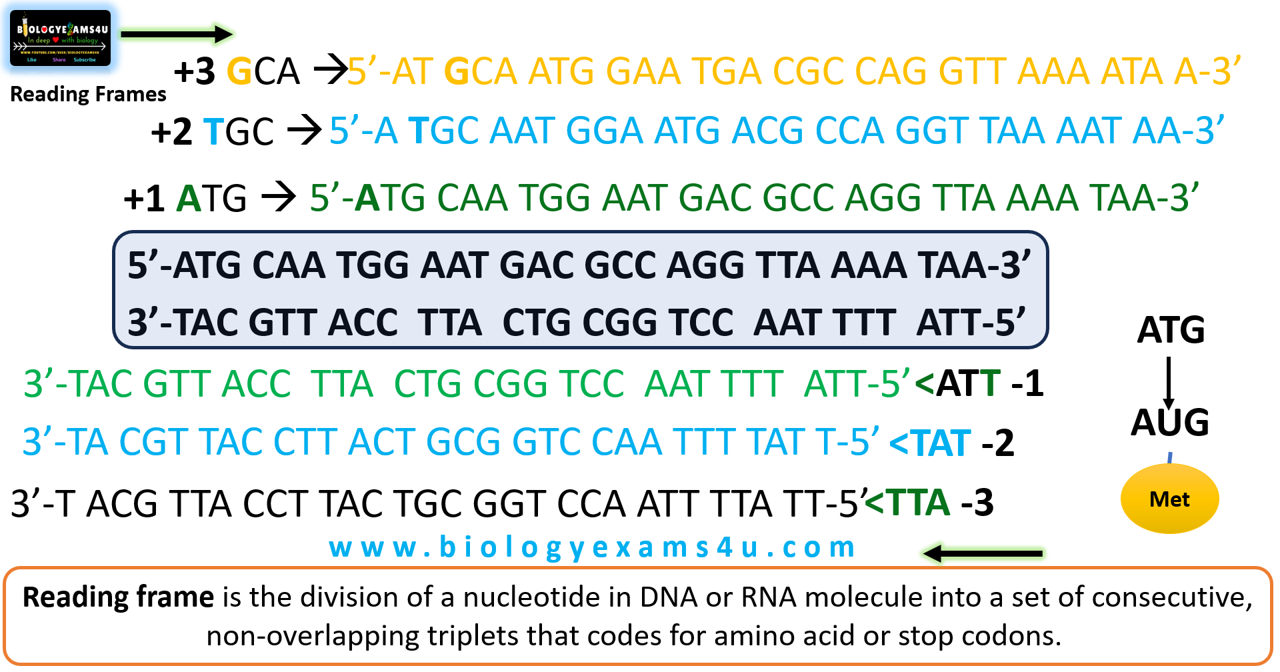
What is a Reading Frame?
Reading frame is the division of a nucleotide in DNA or RNA molecule into a set of consecutive, non-overlapping triplets that codes for amino acid or stop codons.
- Both strands are read in the 5′→3′ direction. Each strand has three reading frames, depending on which nucleotide is selected as the starting position.
- Typically, only one reading frame is used in translating a gene (in eukaryotes), and this is often the longest open reading frame.
You can watch our video here for concept clarity.
What is Open reading frames (ORFs)?
ORF is defined as spans
or stretches of DNA sequence between start and stop codons. An ORF is a reading frame that has the
potential to be transcribed into RNA and translated into protein. It
requires a continuous sequence of DNA from a start codon, multiple of 3
nucleotides, to a stop codon in the same reading frame.
In the above example, for finding out ORF,
- First find the start codon, Here in DNA +1 frame, it is ATG, then the nearest stop codon TAA, TAG, or TGA in DNA (UAA, UAG and UGA in RNA).
- In -1, -2 and -3 frames, there is no ORF
Why
is ORF called “Open”?
The
term “open” refers to the fact that the road is open to keep reading, and the
ribosome will be able to keep reading the RNA code and add another amino acid
one after another, till meeting the stop codon.
Difference
between Reading frame and Open reading frames
The
key difference between a reading frame and an open reading frame is that while
both involve the division of nucleotide sequences into triplets or codons, an
open reading frame specifically refers to a sequence that begins with a start
codon and ends with a stop codon, and has the potential to be transcribed and
translated into a protein. All reading frames may not contain ORF and may not
form a protein.
What
is Coding sequence or CDS?
In
eukaryotes, the genes consist of both introns and exons, therefore ORF of a DNA
sequence or an unprocessed mRNA sequence contains both coding and non-coding
sequences. To annotate the coding sequence, we use conserved splice sites to
find out the coding sequence.
Original image credit: https://www.genome.gov/
But
the processed mRNA has only coding sequence or with only exons, this is called
the coding sequence. A CoDing Sequence (CDS) is a region of DNA or RNA whose
sequence determines the sequence of amino acids in a protein.
Difference
between Open reading frames and Coding
sequence
Open Reading Frame
(ORF), is a continuous stretch of DNA codons that begins with a start codon and
ends at a STOP codon but may contain non coding sequences that are not coding
amino acids.
A CoDing Sequence
(CDS) is a region of DNA or RNA whose sequence determines the sequence of amino
acids in a protein and does not contain introns or non-coding sequence.


Post a Comment
We Love to hear from U :) Leave us a Comment to improve this site
Thanks for Visiting.....