All cells are broadly classified into prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells, according to whether their genetic materials are enclosed by a nuclear envelope or not.
Prokaryotic cells (pro-primitive, karyon- nucleus): From the morphological point of view, prokaryotic cells are the most primitive cells. They do not contain a definite nucleus. The chromatin bodies remain scattered inside the cytoplasm. Such a type of nucleus without a nuclear membrane is called a nucleoid. Eg. bacteria, cyanobacteria (blue green algae) etc.
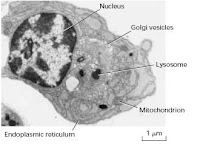
Eukaryotic cells: These are believed to have been evolved from the prokaryotes. They contain a definite nucleus. The chromatin bodies are enclosed by a nuclear membrane. Eukaryotic cells are larger than the prokaryotes. They show better structural organisation and increased functional efficiency than prokaryotes.
Prokaryotic Cell vs Eukaryotic Cell
The size is 0.1- 5.0 um
|
The size is 5-100 um
|
Cell wall, if present, contains mucopeptide or peptidoglycan. Read more: Bacterial Cell wall
|
Cell wall, if present, contains cellulose, peptidoglycan is absent. Read more: Plant cell wall
|
A typical nucleus is absent.
|
A typical nucleus made of nuclear envelope, chromatin,nucleoplasm, nuclear matrix and nucleoli
|
DNA content is low
|
DNA lies inside the nucleus, mitochondria and plastids.
|
DNA is generally circular.
|
DNA is commonly linear
|
DNA is naked or without any association with histone proteins.
|
DNA is associated with histones.
|
Introns are commonly absent in DNA, RNA, therefore, does not require splicing.
|
Introns are quite common. RNA, therefore, requires spicing before becoming operational.
|
Plasmids may occur.
|
Plasmids are rare.
|
Cell membrane may have infolding called mesosome.
|
Mesosome absent
|
Mitochondria are absent
|
Mitochondria are often present
|
Ribosomes are 70 S
|
Ribosomes are 80 S occur in cytoplasm.
|
Cytoplasm does not possess endoplasmic reticulum.
|
Endoplasmic reticulum is usually present.
|
Golgi apparatus is absent
|
Golgi apparatus is present
|
Lysosmes, sphaerosomes and glyoxysomes are absent. | They often present. |
Microtubules and microfilaments are rare.
|
They are usually present.
|
Centrosome is absent
|
Centrosome is present except in flowering plants and a few others.
|
Sexual reproduction is absent.
|
Sexual reproduction is commonly present.
|
Cell division does not show distinction of interphase and M phase
|
A distinction of interphase and mitotic phase occurs during cell cycle.
|
Endocytosis and exocytosis are absent.
|
They occur in eukaryotic cells
|
Flagella are smaller. A distinction of axoneme and sheath is absent in the flagellum.
|
Flagella are longer. A flagellum shows distinction of axoneme and sheath.
|
Cyclosis is absent.
|
Cyclosis or cytoplasmic streaming is common.
|
It may have pili and fimbriae.
|
Pili and fimbriae are absent
|
Transcription occurs in the cytoplasm
|
Transcription occurs inside the nucleus.
|