Cardiac muscle occurs exclusively in the heart. It possess considerable automatic rhythmicity and generates its own wave of excitation. The excitation can also pass directly from fibre to fibre in the cardiac muscle. It is not under voluntary control. It shows cross striations, but striations are much fainter than those of striated muscle. 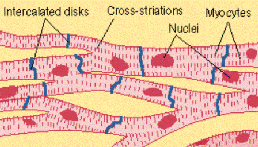
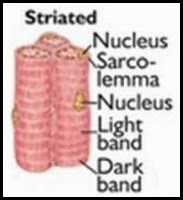
Striated muscle fibres appear to have transverse strips when viewed under the microscope. This is because they show alternative transverse light and dark bands. Most striated muscles are attached to bones by tendons. They are also called skeletal muscles.

Striated muscle fibres appear to have transverse strips when viewed under the microscope. This is because they show alternative transverse light and dark bands. Most striated muscles are attached to bones by tendons. They are also called skeletal muscles.
Cardiac Muscle vs Striated Muscle
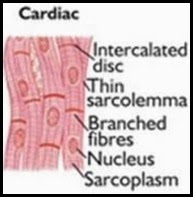
Cardiac Muscle
 |
Striated Muscle
 |
They are present in the wall of the heart, pulmonary veins and superior vena cava.
|
They are present in the limbs, body walls, tongue, pharynx and beginning of oesophagus.
|
Fibres branched.
|
Fibres unbranched.
|
Uninucleate.
|
Multinucleate.
|
Oblique bridges and intercalated discs present.
|
No oblique bridges and intercalated discs.
|
Nerve supply from the brain and autonomic nervous system.
|
Nerve supply from central nervous system.
|
Rapid contraction.
|
Very rapid contraction.
|
They never get fatigued.
|
They soon get fatigued.
|
Involuntary
|
Voluntary
|