DNA is a genetic material which carries all the hereditary information needed for the development and existence of an organism. In prokaryotes, DNA lies in cytoplasm. It is supercoiled with the helps of RNAs and nonhistone basic proteins like polyamines. In eukaryotes it is found mainly in the chromosomes in the form of nucleoproteins. It is also found in the cytoplasmic organelles like mitochondria, chloroplast etc.
Prokaryotic DNA vs Eukaryotic DNA
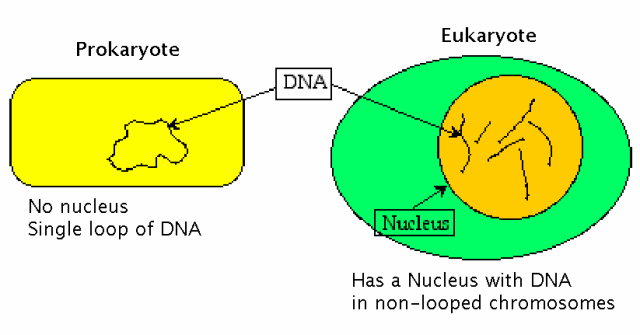
Prokaryotic DNA1. DNA content is small, less 0.1 pg
2. DNA occurs freely inside the cytoplasm.
3. Organelle DNA is absent.
4. It is naked.
5. DNA is generally circular
6. Introns are absent.
7. Nonfunctional regions are fewer
8.Transposons do not occur.
Eukaryotic DNA
1. DNA content is comparatively high, more than 1 pg
2. DNA does not lie freely in the cytoplasm and the most of it is present inside the nucleus.
3. Mitochondrial and plastid (Organelle) DNA present
4. Nuclear DNA is associated with histones while organelle DNA is naked.
5. Nuclear DNA is linear. Organelle DNA may be circular or linear.
6. A cistron contains non coding regions or introns.
7. Nonfunctional DNA is quite abundant.
8. Transposons or jumping genes occur at places.
useful information
ReplyDeleteit was so helpful
ReplyDeleteGreat to know that.. NGS Next Generation Sequencing have changed the meaning of DNA sequencing..... Out there.. many providers are offering NGS Next Generation Sequencing Services.. I think this will give a new builr up for the DNA .. Thanks for sharing.
ReplyDeleteQuite educative
ReplyDeleteThank you so much; this really helped
ReplyDeletevery nice science i like the bit about the science
ReplyDeleteI wouldn't be so sure about Transposons absence in prokaryotes. Check it please
ReplyDeletei learned a lot in their characteristics
ReplyDelete, in their distinctions tnx
Fuck me daddy andy
ReplyDeletePost a Comment
We Love to hear from U :) Leave us a Comment to improve this site
Thanks for Visiting.....