Angiosperms or flowering plants, are the most successful and diversified groups of plants. The angiosperms consist of about 250,000 species of herbs, shrubs, and trees. Most of the plants that are generally seen and dominate the earth belong to this group.
Based on the nature of the embryo in the seed, angiosperms are divided into dicots and monocots.
Monocotyledonae (Monocots) consists of plants having seeds with one cotyledon, and the plants are called monocotyledonous plants.
Example: Grasses, sugarcane, maize, and wheat.
Dicotyledonae (dicots) consists of plants having seeds with two cotyledons, and the plants are called dicotyledonous plants.
Example: Mango, neem, sunflower.
Difference between: Monocotyledonous plants and Dicotyledonous plants
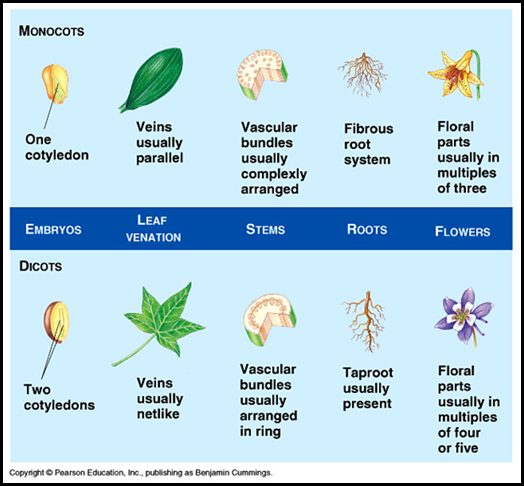
Monocotyledonous plants vs Dicotyledonous plants
Monocotyledonous plants
|
Dicotyledonous plants
|
| Seeds have a single cotyledon. | Seeds have two cotyledons |
| Adventitious root system present. | Tap root system present |
| Leaves have parallel venation. | Leaves have net venation or reticulate venation. |
| Flowers usually incomplete and trimerous (Floral parts are in the number of threes). | Flowers usually complete and pentamerous (floral parts in the number of fives). |
| Vascular bundles in stem are numerous and scattered. | Vascular bundles in stem are fewer and arranged in circles or rings. |
| No cambium, no secondary growth in stem. | Cambium is present, secondary growth occurs. |
| Stem usually hollow. | Stem usually solid |
| Seed germination normally hypogeal | Seed germination either hypogeal or epigeal. |