Klinefelter in 1942 reported an abnormal male syndrome, which came to be known as Klinefelter syndrome. Individuals with this syndromes are phenotypically males but with tendency towards femaleness. They show some abnormal features such as enlarged breasts, underdeveloped body hair, and small testes and prostrate glands. They usually have long legs and hands.
The chromosome complements in most of the affected persons is 47, XXY. They have an extra X in addition to the usual male complement XY(44+XXY). The XXY constitutions originate either by fertilization of an XX egg by Y sperm or an X egg by an exceptional XY sperm. One in every 500 male births is the victim of this syndrome.
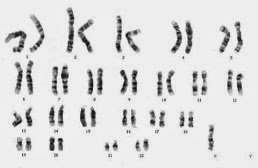
An abnormal human female phenotype, called Turner syndrome, was described by H. H. Turner and associates 1938. It occurs in about 1 per 5000 adult females. The affected adults have virtually no ovaries, lack most sexual characteristics and are sterile. They have short stature, low set ears, webbed neck and shield like chest. Mental deficiency is not associated with this syndrome.
The Turner syndrome is due to monosomy X (45, X). This monosomic has a chromosome complement of 44 autosomes and one X chromosome (44+XO). The abnormal condition probably originates from exceptional egg or sperm with no X chromosome. One in every 3000 females births is a victim.

Isn't one of the female X chromosomes deactivated anyways?
ReplyDeleteThis is incorrect regarding turner Syndrome. People can be Mosaic TS which means not all of their cells are affected. with Mosaic TS you can have some cells (even the majority of your cells be XX), some of your cells can be missing one of the X's and on other cell lines you can actually have a third XXX. People with Mosaic TS are not sexless. They develop breasts, have ovaries and go through puberty normal and can carry their own child in pregnancy. Not everyone has the same characteristics and outward appearances with this chromosomal disorder either. You can normal ears, normal neck, and etc. What characteristics a turner Syndrome girl has depends on how many of her cells were affected. Certain heart defects are common in TS girls and this important fact isn't even mentioned. Also, only 1-2% of Turner Syndrome fetuses are born alive. The other 99% are miscarried early on in the pregnancy or delivered still born. To be alive with this condition is a miracle!!
ReplyDeletePost a Comment
We Love to hear from U :) Leave us a Comment to improve this site
Thanks for Visiting.....